Robust Audio Adversarial Example for a Physical Attack
Hiromu Yakura and Jun Sakuma
University of Tsukuba / RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project
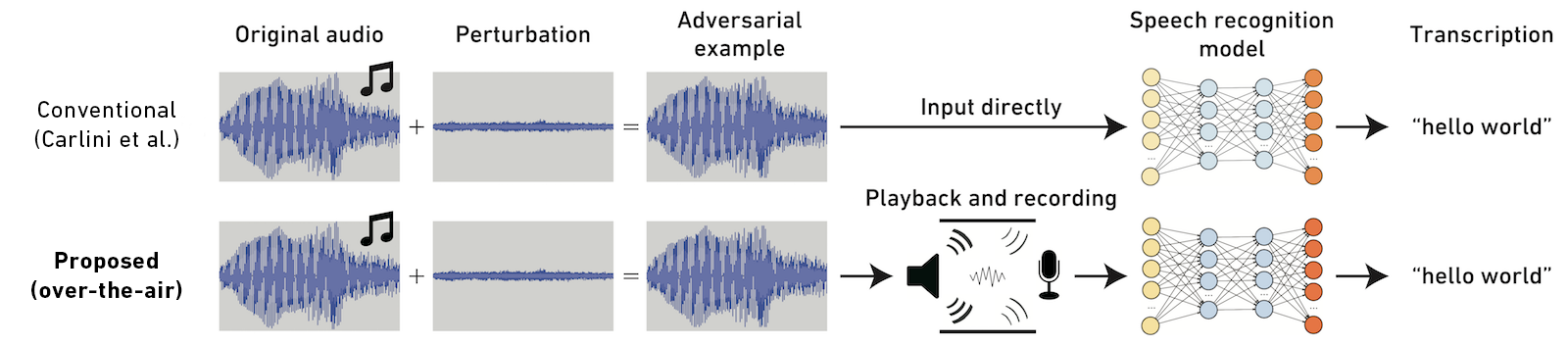

We propose a method to generate audio adversarial examples that can attack a state-of-the-art speech recognition model in the physical world. Previous work assumes that generated adversarial examples are directly fed to the recognition model, and is not able to perform such a physical attack because of reverberation and noise from playback environments. In contrast, our method obtains robust adversarial examples by simulating transformations caused by playback or recording in the physical world and incorporating the transformations into the generation process. Evaluation and a listening experiment demonstrated that our adversarial examples are able to attack without being noticed by humans. This result suggests that audio adversarial examples generated by the proposed method may become a real threat.
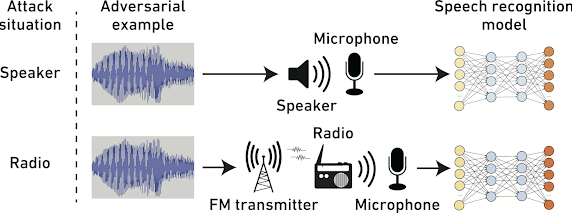
We played and recorded each adversarial example 10 times and evaluated transcriptions by the pretrained model of DeepSpeech. We prepared two different attack situations: speaker and radio.
| Input sample | Target phrase | SNR | Success rate (Speaker) | Success rate (Radio) | Audio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original audio | Bach | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Owl City | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| (A) | Bach | "hello world" | 9.3 dB | 100% | 100% | |
| (B) | Bach | "open the door" | 5.3 dB | 100% | 100% | |
| (C) | Bach | "ok google" | 0.2 dB | 100% | 100% | |
| (D) | Owl City | "hello world" | 11.8 dB | 100% | 100% | |
| (E) | Owl City | "open the door" | 13.4 dB | 100% | 100% | |
| (F) | Owl City | "ok google" | 2.6 dB | 100% | 100% | |
| (G) | Bach | "hello world" | 11.9 dB | 60% | 50% | |
| (H) | Bach | "open the door" | 6.6 dB | 60% | 60% | |
| (I) | Bach | "ok google" | 4.2 dB | 80% | 70% | |
| (J) | Owl City | "hello world" | 12.2 dB | 70% | 50% | |
| (K) | Owl City | "open the door" | 14.6 dB | 90% | 100% | |
| (L) | Owl City | "ok google" | 8.7 dB | 90% | 70% |
| Attack on recurrent models | Attack over the air | Audio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carlini et al. (2018) | ✔ | ||
| Yuan et al. (2018) | ✔ | ||
| Proposed | ✔ | ✔ | (above) |

|
Hiromu Yakura and Jun Sakuma: Robust Audio Adversarial Example for a Physical Attack.
In Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019. [Paper] [arXiv:1810.11793] |
This study was supported by JST CREST JPMJCR1302 and KAKENHI 16H02864.